Phosphate Buffer System Equation
Phosphate buffer system equation. Phosphates sequester divalent cations such as Ca2 and Mg2. The Phosphate Buffer System. PH calculations for buffer systems are performed using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
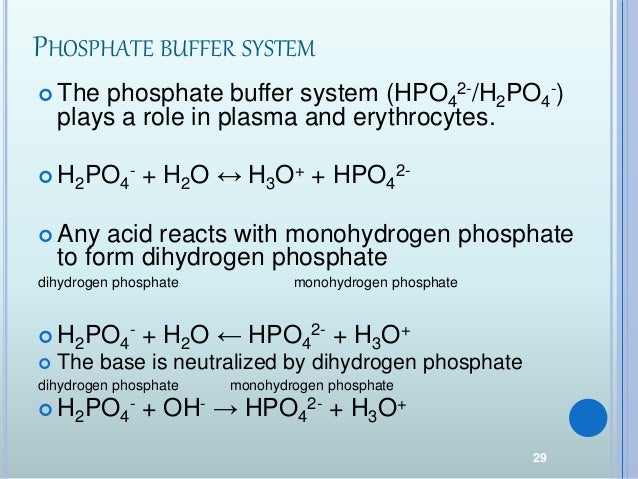
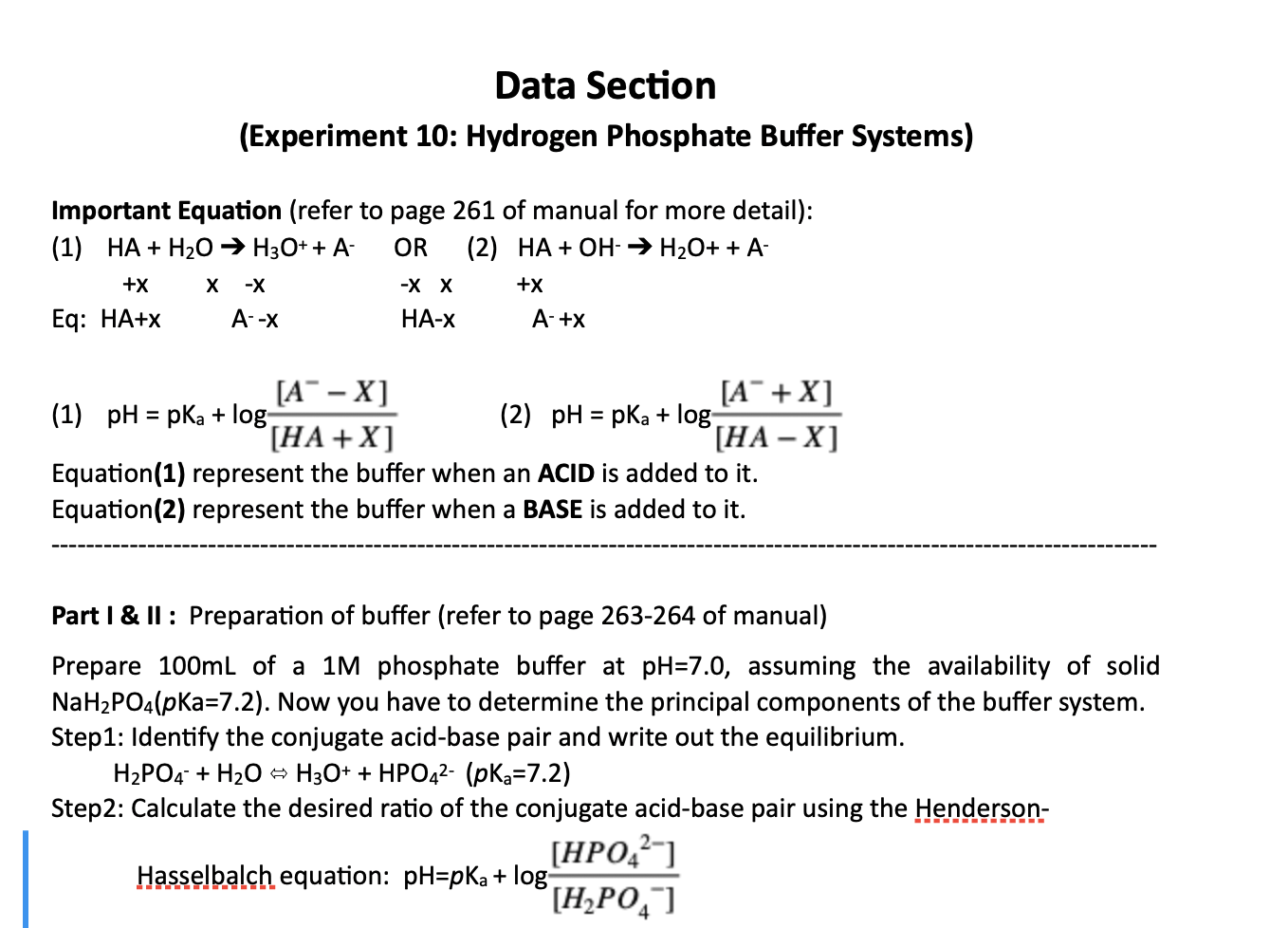
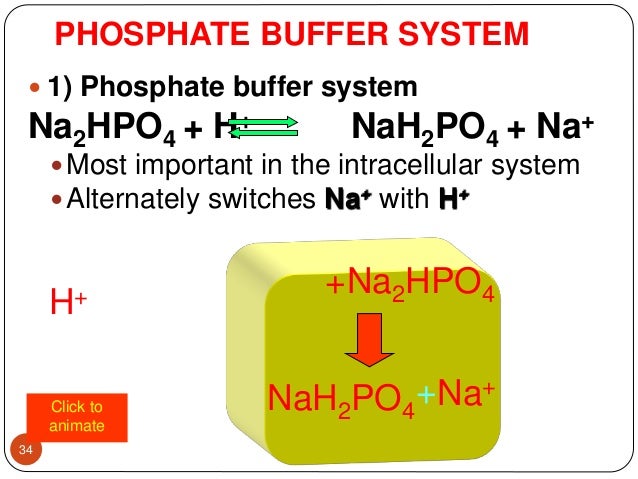
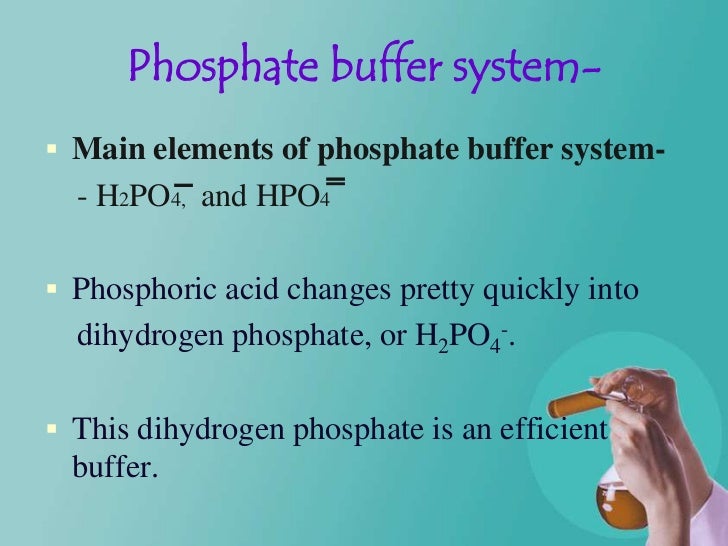
The main elements of the phosphate buffer system are H2PO4- and HPO4. Because phosphates precipitate in ethanol it is not possible to precipitate DNA and RNA from buffers that contain significant quantities of phosphate ions. Select the pKa value that is closest to the pH of your buffer.
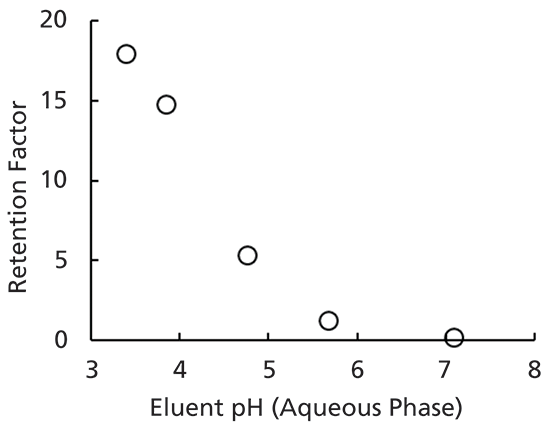
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation can be applied to tell us the proportions of dihydrogen phosphate and monohydrogen phosphate present in a buffered system between pH 4 and 10. The phosphate buffer system operates in the internal fluid of all cells. Each of these three equilibrium equations can be expressed mathematically in several different ways.
The Phosphate Buffer This buffer system acts in a similar manner as the bicarbonate buffer system. Buffer Preparation Formulas and Equations Percentage by weight wv buffer desired 100 final buffer volume mL g of starting material needed. K2 62 x 10-8.
An equation that could calculate the pH value of a given buffer solution was first derived by the American chemist Lawrence Joseph Henderson. Normal blood pH is 735 to 745 and pH values outside the 70 to 78 range are life-threatening. Desired molarity formula weight solution final volume L grams needed.
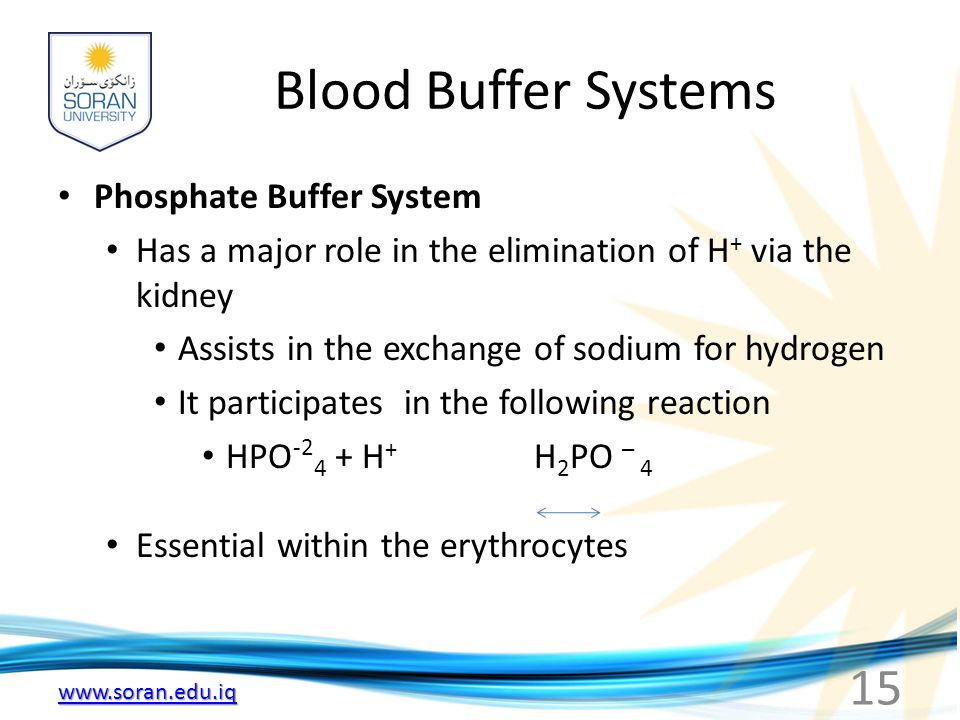
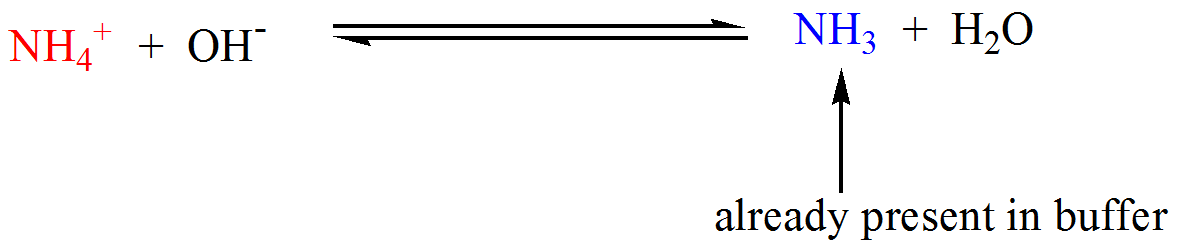
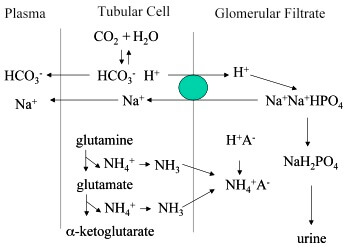
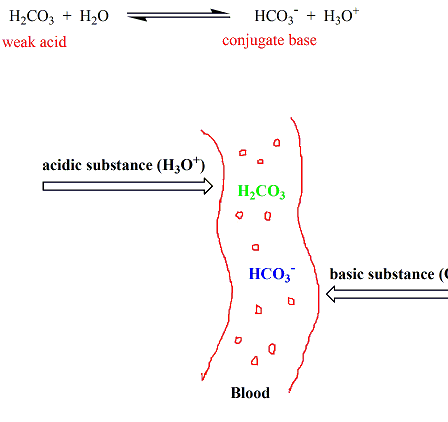
Phosphates are found in the blood in two forms. Thus phosphate equilibrium in plasma is such that 4 parts of the so-called basic phosphate HPO 2 4 exists to 1 part of acidic phosphate H 2 PO 4 at a pH of 74 for pK phos is 68. A modified version of the HendersonHasselbalch equation can be used to relate the pH of blood to constituents of the bicarbonate buffer system.
Buffer Preparation Formulas and Equations Percentage by weight wv buffer desired 100 final buffer volume mL g of starting material needed. A simple phosphate buffer is used ubiquitously in biological experiments as it can be adapted to a variety of pH levels including isotonic.
The main elements of the phosphate buffer system are H2PO4- and HPO4.
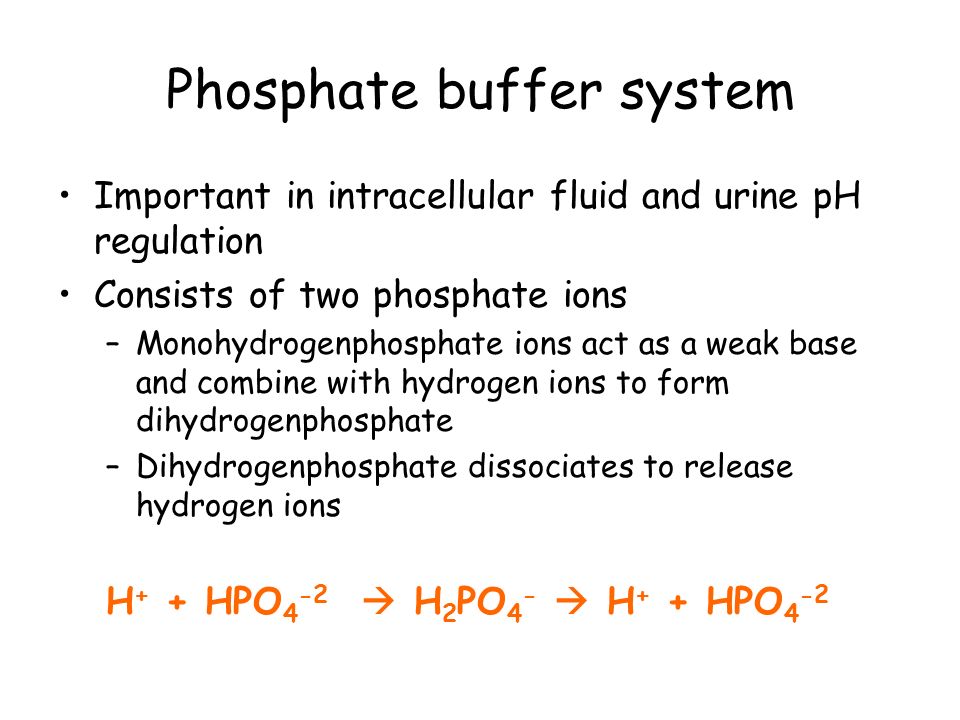
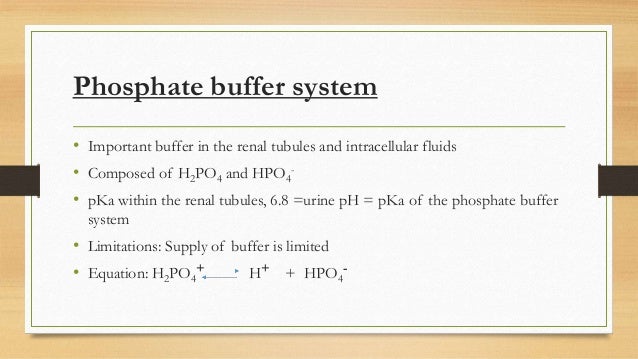
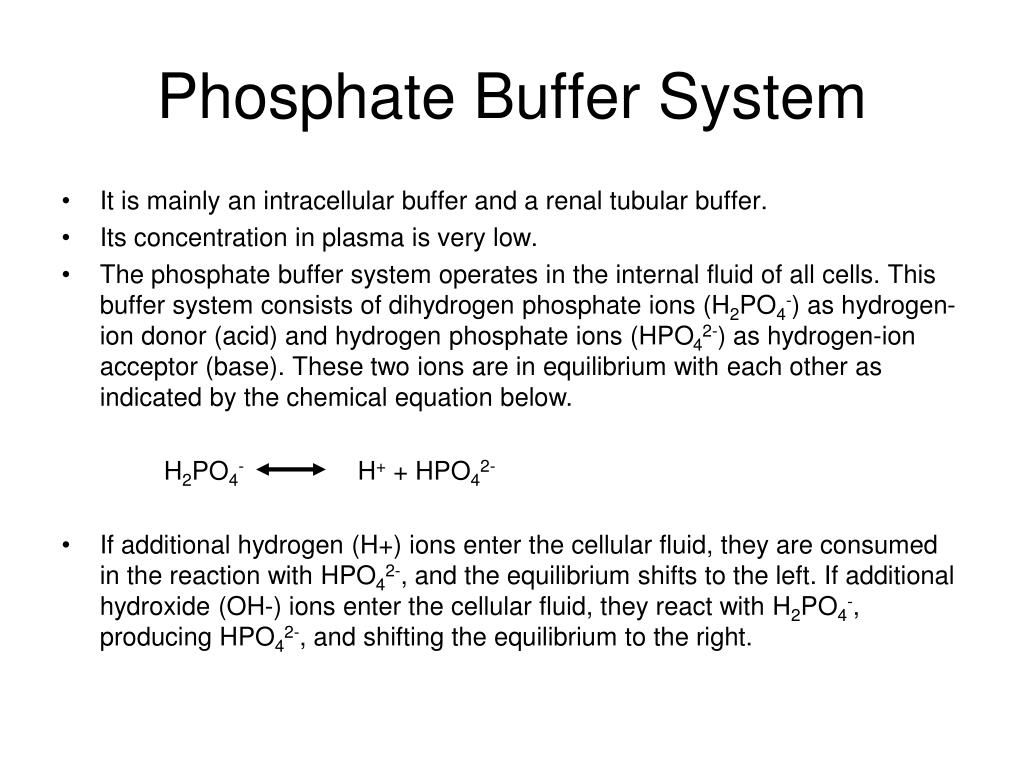
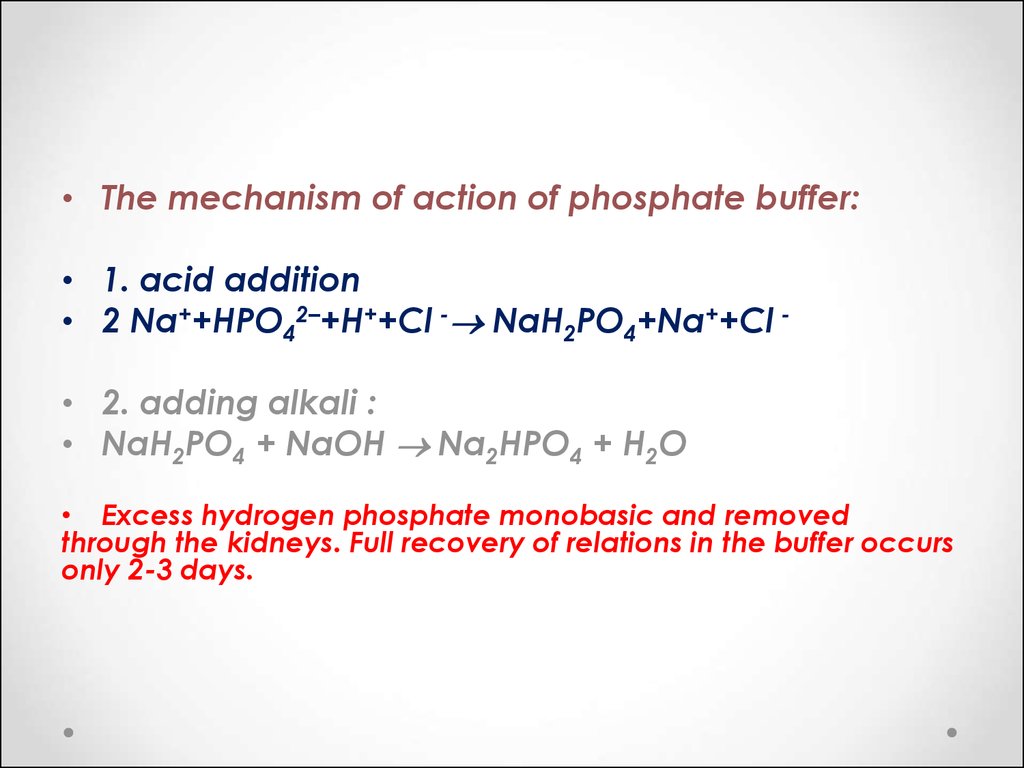
These two ions are in equilibrium with each other as indicated by the chemical equation given below. Buffer Preparation Formulas and Equations Percentage by weight wv buffer desired 100 final buffer volume mL g of starting material needed. Sodium dihydrogen phosphate Na 2 H 2 PO 4 which is a weak acid and sodium monohydrogen phosphate Na 2 HPO4 2- which is a weak base. This buffer system consists of dihydrogen phosphate ions H 2 PO 4 as hydrogen ion donor acid and hydrogen phosphate ions HPO 2-4 as hydrogen-ion acceptor base. For these three we only need three equations. For example if you want the pH of your buffer to be 7 then use the pKa of 69. Each of these three equilibrium equations can be expressed mathematically in several different ways. That is because the buffering capacity of a phosphate buffer is pH 721 1 within which most of the proteins and enzymes are more stable. The pK of the inorganic phosphate buffer is 68 providing excellent buffering capacity around the normal ECF pH of 74.
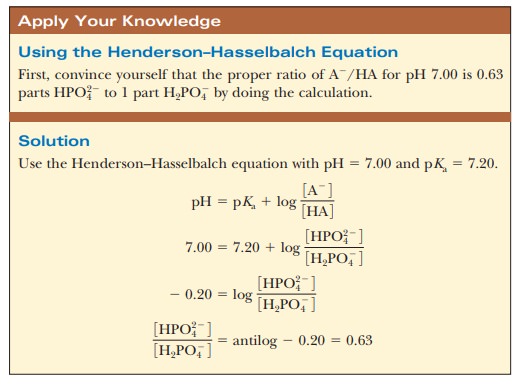
K2 62 x 10-8. Other buffers perform a more minor role than the carbonic-acid-bicarbonate buffer in regulating the pH of the blood. A modified version of the HendersonHasselbalch equation can be used to relate the pH of blood to constituents of the bicarbonate buffer system. In order to calculate the pH of a PBS buffer you can use the Hendeson-Hasselbalch equation pH_sol pK_a logconj baseweak acid In your case you have pH_sol pK_a logHPO_42-H_2PO_4- To get the pK_a you need the value of the acid dissociation constant K_a for dihydrogen phosphate. The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation for this buffer system may be written as. The Phosphate Buffer This buffer system acts in a similar manner as the bicarbonate buffer system. The pK of the inorganic phosphate buffer is 68 providing excellent buffering capacity around the normal ECF pH of 74.
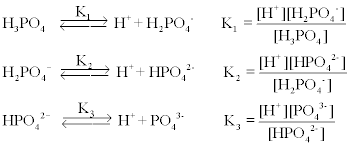
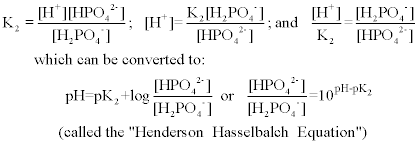













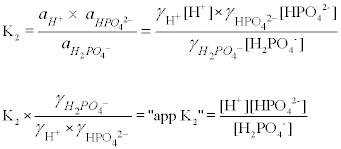






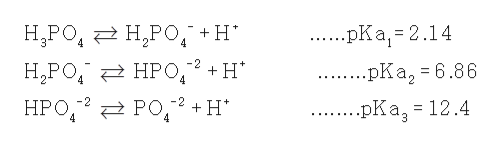




Post a Comment for "Phosphate Buffer System Equation"